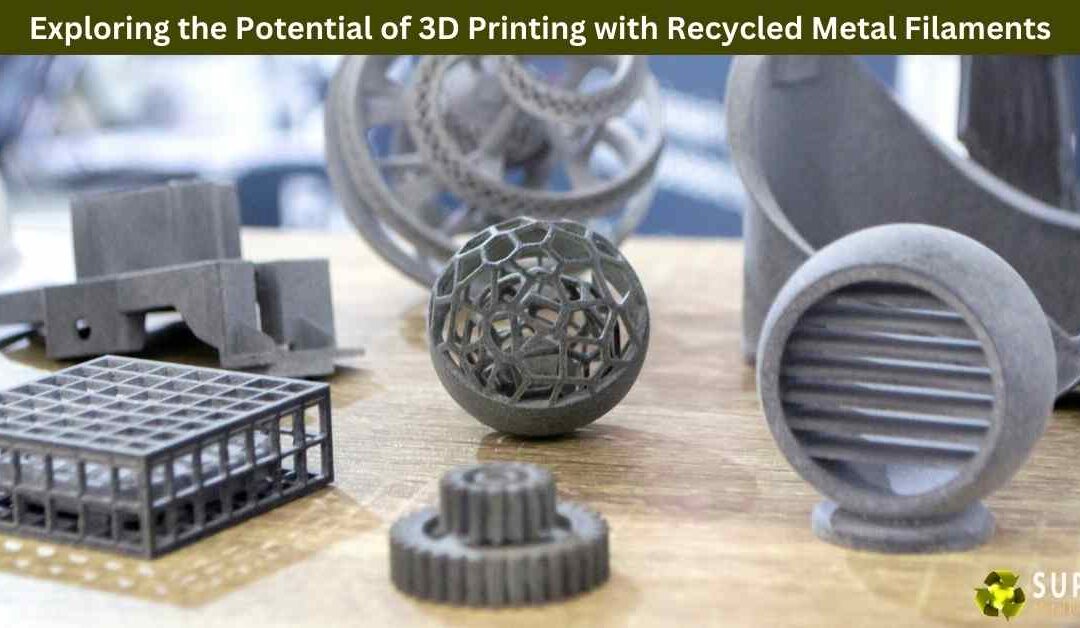
The advent of 3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing, enabling the creation of complex and customized objects with unprecedented precision and speed. As this technology continues to evolve, so too does the exploration of sustainable materials that can be used in the process. One of the most exciting developments in this space is the use of recycled metal filaments for 3D printing. This innovation not only opens up new possibilities for manufacturing but also offers significant environmental benefits. In this blog, we’ll delve into the potential of 3D printing with recycled metal filaments, exploring its applications, advantages, and the challenges that lie ahead.
The Rise of 3D Printing and Metal Filaments
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer from digital models. Originally, 3D printing was primarily associated with plastics, but as the technology has matured, the range of materials available for printing has expanded to include metals. Metal 3D printing has been used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, for producing complex parts that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
Metal filaments, which are used in some types of 3D printers, are typically made by combining metal powders with a binding material. The filament is fed into the printer, which melts and extrudes it layer by layer to form the desired object. Once printed, the object may undergo additional processing, such as sintering, to strengthen and finalize the material.
The Sustainability Factor: Recycled Metal Filaments
The environmental impact of manufacturing has become a significant concern in recent years, driving the demand for more sustainable practices and materials. Recycled metal filaments represent a promising solution to this challenge, as they combine the benefits of metal 3D printing with the advantages of recycling.
Recycled metal filaments are made from scrap metal, which is collected, processed, and converted into a usable form for 3D printing. This process not only diverts waste from landfills but also reduces the need for new raw materials, conserving natural resources and lowering the carbon footprint of manufacturing.
Applications of 3D Printing with Recycled Metal Filaments
The use of recycled metal filaments in 3D printing is still in its early stages, but it holds great potential for a wide range of applications. Some of the most promising areas include:
Prototyping and Custom Manufacturing
3D printing with recycled metal filaments is ideal for creating prototypes and custom parts that require the strength and durability of metal. This approach is particularly useful in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and material properties are critical. By using recycled materials, companies can reduce costs and environmental impact while still achieving high-quality results.
Sustainable Architecture and Construction
The construction industry is increasingly exploring 3D printing as a way to create complex structures with less waste and more design flexibility. Recycled metal filaments can be used to print components for buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional construction materials. This could lead to the development of greener cities and more efficient use of resources in urban development.
Art and Design
Artists and designers are often at the forefront of experimenting with new materials and techniques. Recycled metal filaments offer a unique medium for creating sculptures, jewelry, and other decorative objects. The ability to print intricate designs with metal adds a new dimension to creative expression, while the use of recycled materials aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the art world.
Medical Devices and Implants
In the medical field, 3D printing with metal has been used to create implants, prosthetics, and other devices that are customized to fit individual patients. Recycled metal filaments could make these products more affordable and environmentally friendly, particularly in regions where access to medical supplies is limited. The ability to produce high-quality medical devices from recycled materials could have a profound impact on global healthcare.
Advantages of Using Recycled Metal Filaments
The use of recycled metal filaments in 3D printing offers several key advantages:
- Environmental Benefits: By using recycled materials, manufacturers can reduce waste, conserve resources, and lower their carbon footprint. This is particularly important in industries where sustainability is a growing concern.
- Cost Savings: Recycled metal filaments can be more cost-effective than virgin materials, especially in applications where the material’s performance is not compromised by the recycling process. This can make 3D printing more accessible to smaller companies and individuals.
- Resource Efficiency: The production of recycled metal filaments requires less energy and fewer raw materials than the production of new metals. This contributes to a more efficient and sustainable manufacturing process.
- Versatility: Recycled metal filaments can be used in a variety of applications, from industrial manufacturing to artistic projects. This versatility makes them an attractive option for a wide range of industries.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the potential of 3D printing with recycled metal filaments is exciting, there are also challenges that need to be addressed:
- Material Consistency: Ensuring the consistency and quality of recycled metal filaments can be challenging, as the properties of recycled materials can vary depending on their source and processing. Advances in material science and quality control are needed to address this issue.
- Processing Techniques: The process of converting scrap metal into a filament suitable for 3D printing is still being refined. This includes developing efficient methods for shredding, melting, and extruding the metal, as well as improving the binding materials used in the filaments.
- Market Adoption: While there is growing interest in sustainable manufacturing, widespread adoption of recycled metal filaments will require education, incentives, and industry collaboration. Manufacturers need to be convinced of the benefits and reliability of these materials.
Despite these challenges, the future of 3D printing with recycled metal filaments looks promising. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see more widespread use of these materials in a variety of applications. The development of new alloys, improved processing techniques, and greater industry collaboration will help to unlock the full potential of this innovative approach to sustainable manufacturing.
Conclusion
3D printing with recycled metal filaments represents a significant step forward in the quest for more sustainable manufacturing practices. By combining the versatility and precision of 3D printing with the environmental benefits of recycling, this technology offers a powerful tool for reducing waste, conserving resources, and lowering the carbon footprint of industrial activities. As the industry continues to evolve, recycled metal filaments have the potential to become a cornerstone of sustainable manufacturing, paving the way for a greener and more efficient future.
If you are in Doveton, Victoria 3177, and looking for a metal recycling service, this is the best way to visit us.
345 Frankston – Dandenong Road, Dandenong South VIC 3175
(03) 9706 4909

Recent Comments